glossary
Modified from Ouvard et al. (2000).
Helix (stem)
A right-handed double helix composed of a succession of complementary hydrogen-bonded nucleotides between paired strands. 
Single strand (loop)
Unpaired nucleotides separating helices.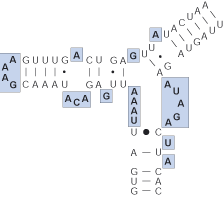
Hairpin-stem loop
Helix closed distally by a loop of unpaired nucleotides (terminal bulge).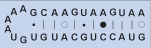
Terminal bulge
Succession of unpaired nucleotides at the end of a hairpin-stem loop.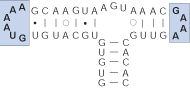
Lateral bulge
Succession of unpaired nucleotides on one strand of a helix.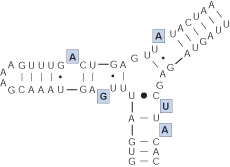
Internal bulge
Group of nucleotides from two antiparallel strands unable to form canonical pairs.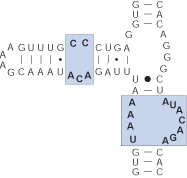
Compensatory base change (CBC)
Subsequent mutation on one strand of a helix to maintain structure following initial mutation of a complementary base.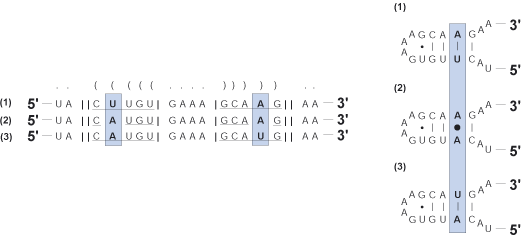
Insertion
A single insertion of a nucleotide relative to the rest of the multiple sequence alignment.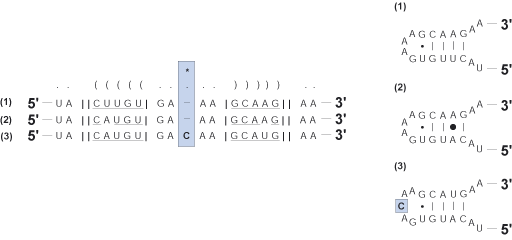
Deletion
A single deletion of a nucleotide relative to the rest of the multiple sequence alignment.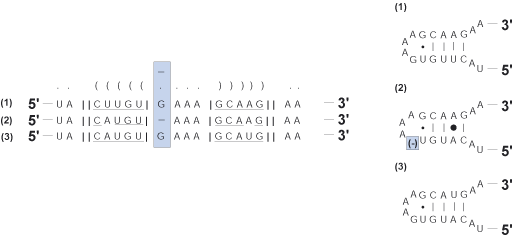
Indel
An ambiguous position within a multiple sequence alignment that cannot be described as an insertion or deletion. RAAs, RSCs, and RECs are all examples of indels.
Region of ambiguous alignment (RAA)
Two or more adjacent, non-pairing positions within a sequence wherein
positional homology cannot be confidently assigned due to the high occurrence of indels in other sequences.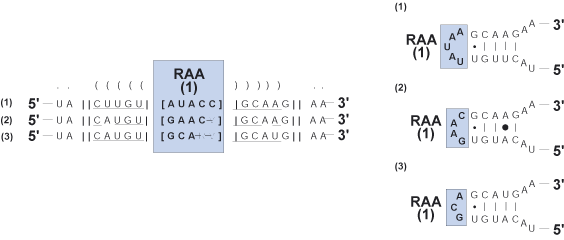
Region of slipped-strand compensation (RSC)
Region involved in base-pairing wherein positional homology cannot be defended across a multiple sequence alignment; inconsistency in pairing likely due to slipped-strand mispairing.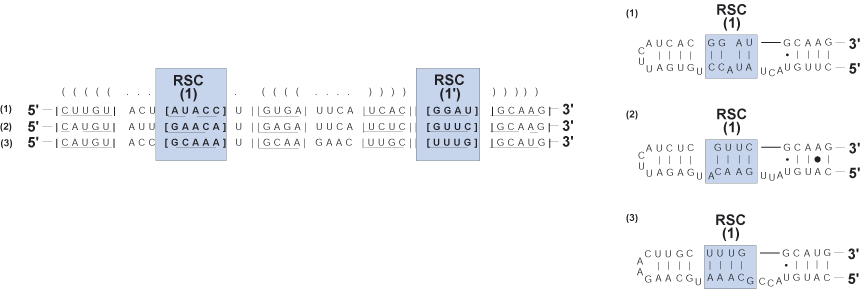
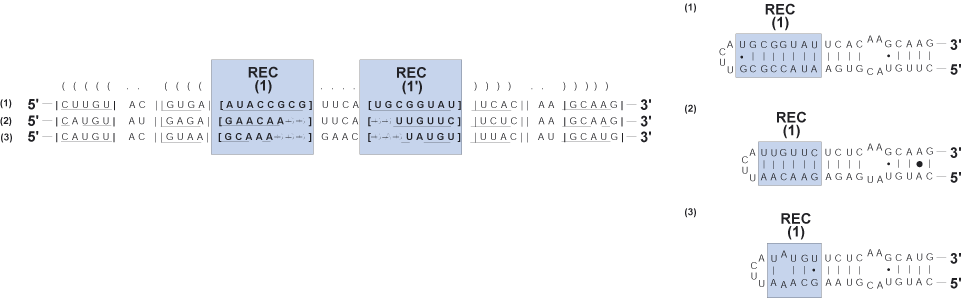
Region of expansion and contraction (REC)
Variable helical region flanked by conserved basepairs at the 5' and 3' ends, and an unpaired terminal bulge of at least three nucleotides;
characteristic of RNA hairpin-stem loops.